Fast Deployment & Reduced Rime-to-Market
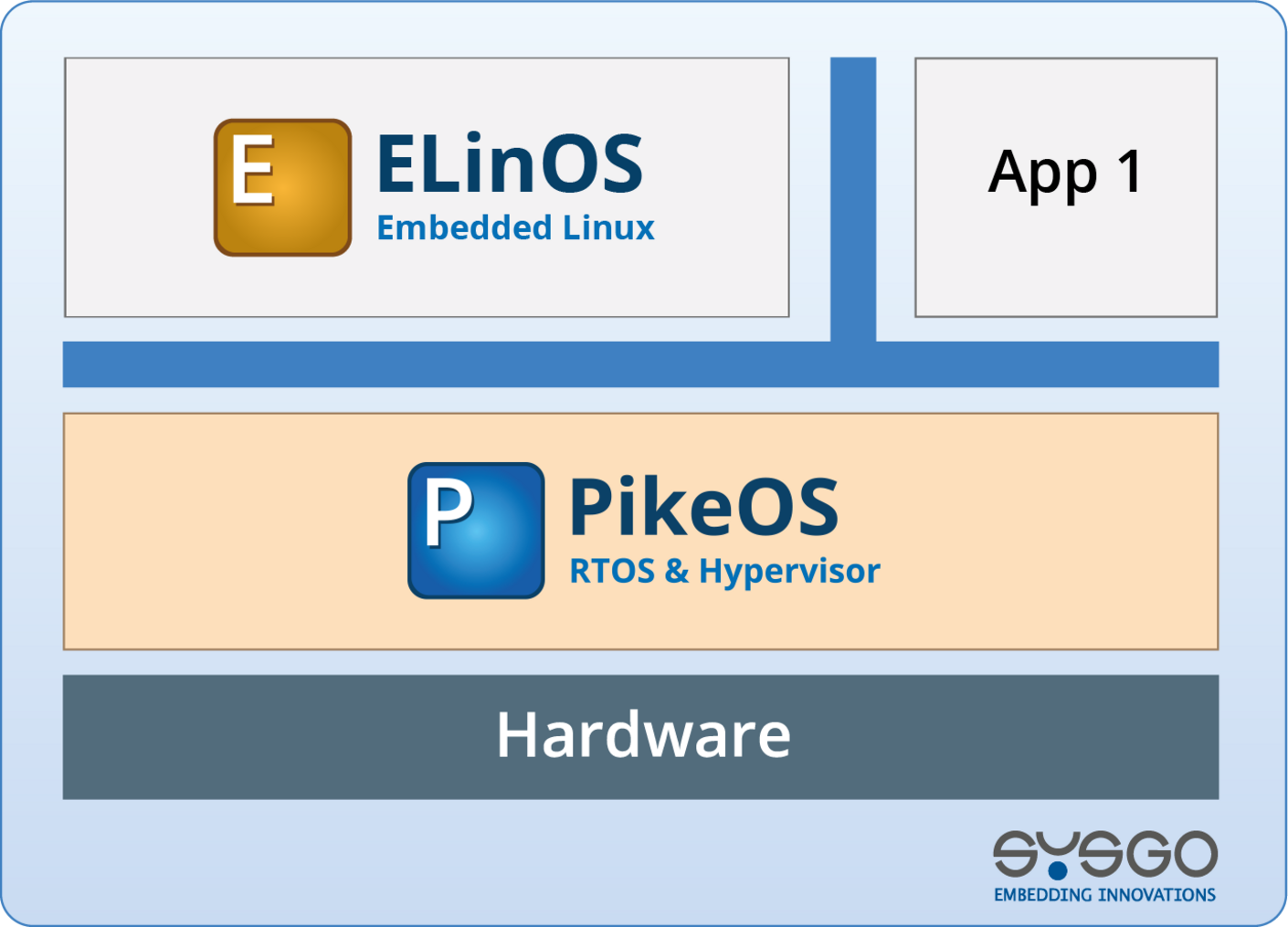
ELinOS integrates seamlessly into PikeOS partitions, allowing rapid system setup and reducing development cycle time
Strict Isolation and Partition Safety
PikeOS enforces spatial and temporal separation between partitions, so ELinOS guests cannot affect higher-criticality applications—even if ELinOS crashes, it stays isolated
Flexibility in System Architecture
ELinOS runs side-by-side with POSIX APIs, ARINC 653 partitions, or certified PikeOS native apps—enabling hybrid designs in one platform
Optimized Virtualization Performance
With hardware virtualization, ELinOS achieves near-native performance, especially for system calls and interrupt handling—benchmarks show minimal overhead vs. bare-metal execution
No BSP required for Guest Mode
As a PikeOS guest, ELinOS requires no dedicated BSP. It runs independently of the physical hardware configuration, reducing integration complexity
Unified IDE Experience
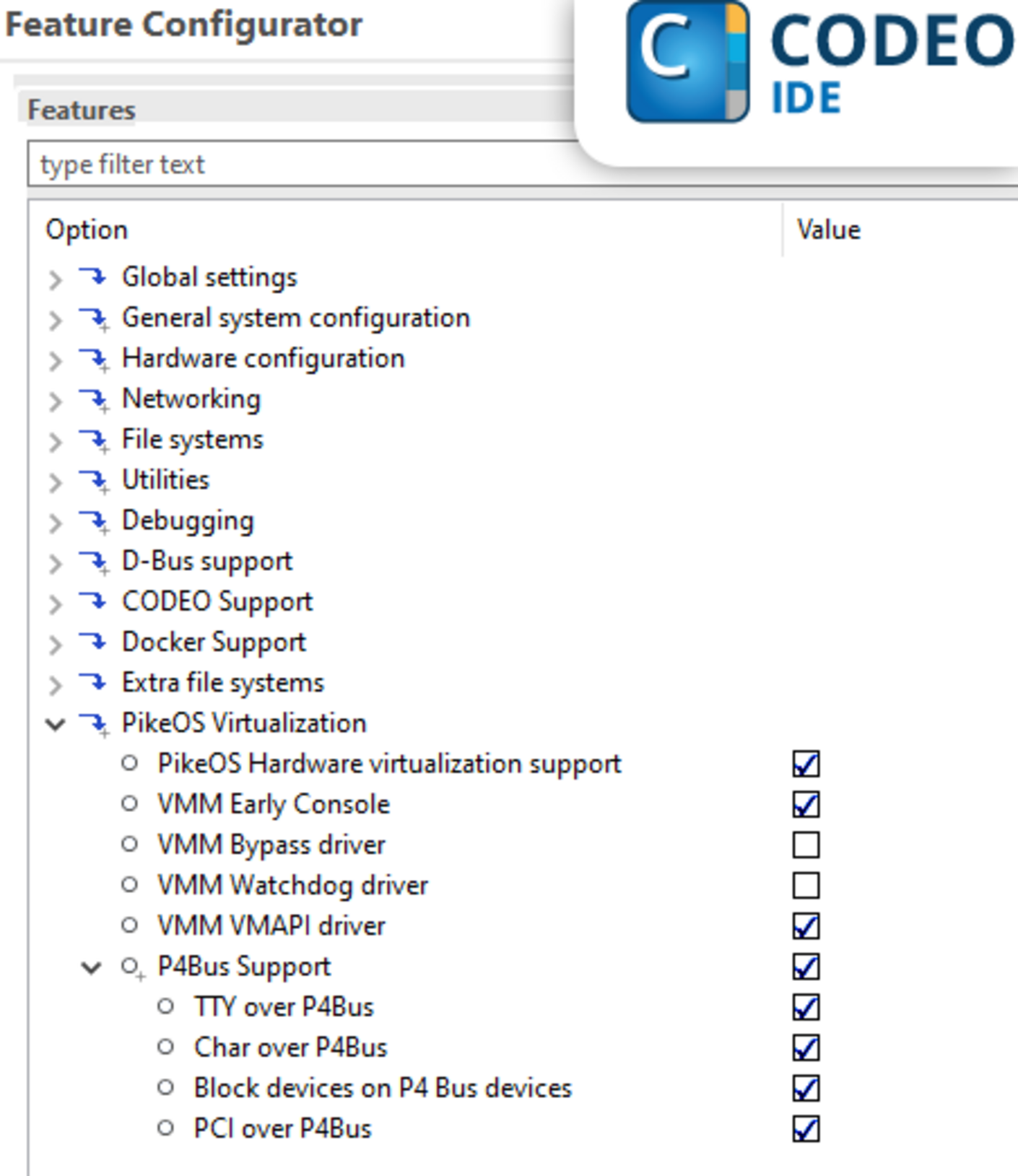
CODEO provides a common toolchain for both PikeOS and ELinOS development—including configuration, debugging, and image management—with a consistent UI and workflow